了解几个概念
- Selector(typedef struct objc_selector *SEL):在运行时Selectors用来代表一个方法的名字。Selector是一个在运行时被注册(或映射)的C类型字符串。Selector由编译期产生并且在当类被加载进内存时由运行时自动进行名字和实现的映射。
- Method(typedef struct objc_method *Method):是一个不透明的用来代表一个方法的定义的类型。
- Implementation(typedef id(*IMP)(id,SEL,…)):这个数据类型指向一个方法的实现的最开始的地方。该方法为当前CPU架构使用标准的C方法调用来实现。该方法的第一个参数指向调用方法的自身(即内存中类的实例对象,若是调用类方法,该指针则是指向元类对象(metaclass));第二个参数是这个方法的名字Selector,该方法的真正参数紧随其后。
理解Selector,Method,Implementation这三个概念之间关系的最好方式是:在运行时,类(Class)维护了一个消息分发列表来解决消息的正确发送。每一个消息列表的入口是一个方法(Method),这个方法映射了一对键值对,其中键值是这个方法的名字Selector(SEL),值是指向这个方法实现的函数指针Implementation(IMP)。Method Swizzling修改了类的消息分发列表使得已经存在的Selector映射了另一个Implementation,同时重命名了原生方法的实现为一个新的Selector。
Method Swizzling原理
Method Swizzling是发生在运行时的,主要用于在运行时将两个Method进行交换,Method Swizzling配合类别可以实现在不干扰其他工程代码的情况下与系统的方法进行交换。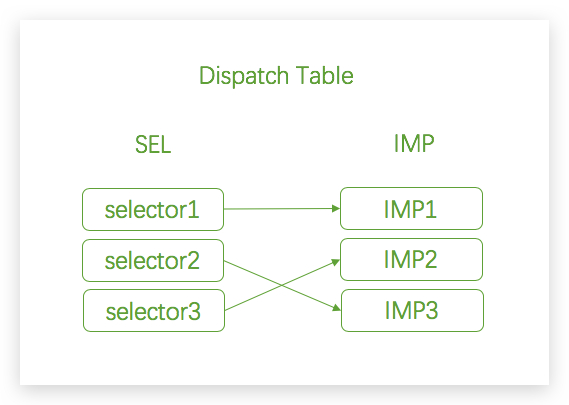
在上图中,我们添加了selector3和IMP3,并让selector2指向了IMP3,而selector3则指向了IMP2,这样就实现了“方法交换”。
在Objective-C的runtime特性中,调用一个对象的方法就是给这个对象发送消息。是通过查找接收消息对象的方法列表,从方法列表中查找对应的SEL,这个SEL对应着一个IMP(一个IMP可以对应多个SEL),通过这个IMP找到对应的方法调用。
每个类中都有一个Dispatch Table,这个Dispatch Table本质是将类中的SEL和IMP进行对应。而我们的Method Swizzling就是对这个table进行了操作,让SEL对应另一个IMP。
Method Swizzling用法
先给要交换的方法的类添加一个Category,然后在Category中的+(void)load(iOS开发 - +load 和 +initialize 方法) 方法中添加Method Swizzling方法,我们用来交换的方法也写在Category中。
两种使用方式:
- 第1种:
1 | class_getInstanceMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name) |
- 第2种:
1 | method_exchangeImplementations(Method _Nonnull m1, Method _Nonnull m2) |
应用举例
- 打印当前进入的controller的名称。为了方便日常开发的调试,我们可以交换系统viewDidLoad方法的实现,在新的方法中,打印当前控制器的名称,方便我们定位当前页面对应的controller。当然,线上版本并不需要,因此要打上DEBUG。
1 | + (void)load { |
- 防止popToViewController方法,找不到对应的controller时,导致crash。
1 | + (void)load { |
- 防止因为数组越界而导致的crash(不推荐,有问题)
在iOS中NSNumber、NSArray、NSDictionary等这些类都是类簇(Class Clusters),一个NSArray的实现可能由多个类组成。所以如果想对NSArray进行Swizzling,必须获取到其“真身”进行Swizzling,直接对NSArray进行操作是无效的。这是因为Method Swizzling对NSArray这些的类簇是不起作用的。
因为这些类簇类,其实是一种抽象工厂的设计模式。抽象工厂内部有很多其他继承自当前类的子类,抽象工厂类会根据不同情况,创建不同的抽象对象来进行使用。例如我们调用NSArray的objectAtIndex:方法,这个类会在方法内部判断,内部创建不同抽象类进行操作。
所以如果我们对NSArray类进行Swizzling操作其实只是对父类进行了操作,在NSArray内部会创建其他子类来执行操作,真正执行Swizzling操作的并不是NSArray自身,所以我们应该对其“真身”进行操作。
下面列举了NSArray和NSDictionary本类的类名,可以通过Runtime函数取出本类:
| 类名 | 真身 |
|---|---|
| NSArray | __NSArrayI |
| NSMutableArray | __NSArrayM |
| NSDictionary | __NSDictionaryI |
| NSMutableDictionary | __NSDictionaryM |
1 | + (void)load { |
这里需要注意:
- 当创建的数组,为空时,其class为NSArray0,当数组只有一个元素时,其class为NSSingleObjectArrayI,其他情况下,其class才为__NSArrayI。因此使用上述的方法进行防止crash时,需要考虑使用。因此不推荐该方法。
- 为何在交换的方法中,调用该方法,为何不调用原交换方法?因为系统的方法已经被我们交换了,因此我们写的交换方法的SEL指向的其实是系统原来的方法,如果我们再调用原交换方法的话,就会造成死循环了。这里需要注意!